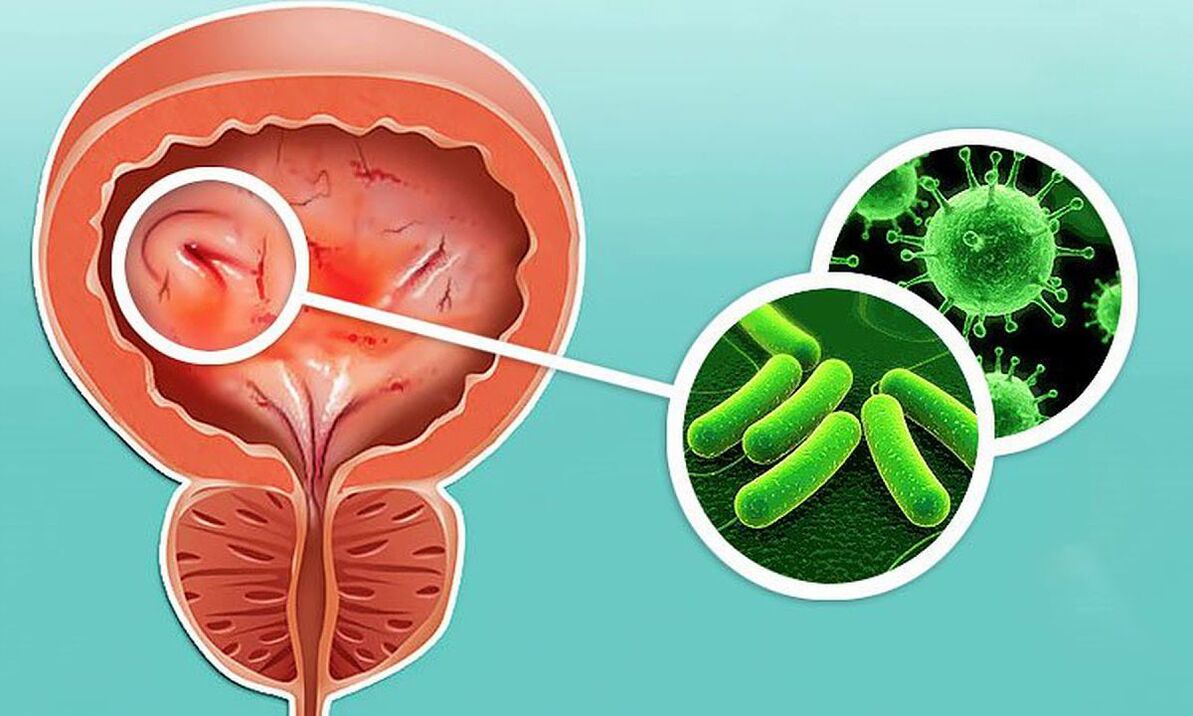
Cyctitis is a common disease of the urinary system, which is related to the inflammatory process of the bladder mucosa. Notably, one in four women faces symptoms of cystitis at least once in their lifetime, and one in 10 suffers from a chronic form of the disease. The incidence in women and men is also worth comparing: only 0. 5% of men have cystitis, mainly due to differences in the structure of the urinary tract and the difficulty of infection.
cause of disease
Cystitis in women is usually due to invasive opportunistic pathogens entering the urethra, as well as ascending sexually transmitted infections: chlamydia, Ureaplasma, and Candida fungal infections. Short, wide urethra are often susceptible to this infection. Cystitis in women can also occur due to the movement of pathogens in the blood. The path of development of this disease is called hematogenous.
Another option for infection is the entry of bacteria into the bladder with kidney and ureteral lesions. The development of this event can usually be observed in pyelonephritis.

A less common but still occurring variant of disease development should be noted, caused by dysplasia of the urinary system. In addition, decreased bladder muscle contractions can lead to cystitis.
Signs of infection are especially active in the presence of predisposing factors. These include:
- Sedentary work. Sitting for more than three hours in a row can stagnate urine, which can lead to bladder infections. So if your job involves sitting in one place for long periods of time, you need to get up every hour and do a little warm-up every three hours.
- constipate.
- Sand and stones are present in the bladder.
- Tight underwear that disrupts normal blood circulation to the pelvic organs.
- The body is often hypothermic.
- Lower back injury, spinal cord injury.
- Early onset of sexual activity.
- Metabolic disorders, hormonal changes in the body (eg, menopause or pregnancy). During a hormonal surge, the body's immune system malfunctions. Please note: Expectant mothers are especially at risk of infection and cystitis when they are pregnant with a baby. Therefore, during pregnancy, you must monitor your health carefully and consult your doctor at the first sign of illness.
- Diabetes (diabetes).
- Treat with immunosuppressants.
- tumor disease.
- Unbalanced and irregular nutrition: Abuse of spicy and fried foods, alcoholism.
- Improper hygiene procedures (especially improper washing from anus to vagina).
- Inadequate personal hygiene (using the same sanitary pad or tampon for a long period of time, not changing underwear in time, using sanitary pads frequently) has a high chance of bladder infection.
- High stress and long-term lack of sleep will seriously affect the immune status.
- Immunity is generally weakened due to the presence of chronic inflammatory lesions (Stomatitis, Caries, Rhinitis, Tonsillitis) in the body. Therefore, this can lead to violation of urethral infertility
In addition, it is worth emphasizing that bladder inflammation such as interstitial cystitis, which is the result of severe dysfunction of the immune system, is a serious chronic disease.
symptoms and signs

The symptoms of cystitis are very typical and allow you to make a correct diagnosis right away. First, these are frequent urination (the patient goes to the toilet several times an hour) and pain manifestations at the end of the bladder emptying process. In addition, the most notable symptoms include:
- Feeling of full bladder even after urinating;
- urine mixed with blood or pus;
- Urine smells more pungent in women with cystitis;
- cloudy urine and flakes in it;
- lower abdominal pain;
- Kidney and lower back pain may occur when the infection spreads to the upper urinary system;
- fairly rare, but still have difficulty holding urine
If you notice these symptoms on yourself, you should consult a doctor for diagnosis and further treatment, as advanced forms of the disease are fraught with many complications.
The symptoms of cystitis bring not only physical but psychological discomfort to a woman, leaving a mark on her personal and social life. Therefore, it is necessary to respond as soon as possible to the appearance of the first signs of the disease and start treatment.
Interstitial cystitis, already mentioned above, may occur if the inflammation caused by the infection is passed to the muscular layer of the bladder. In this case, urine is introduced into the wall of the organ and back up into the ureter.

If left untreated and the infection spreads vertically, kidney disease and pyelonephritis may develop.
Types of Cystitis
It is necessary to distinguish the types of diseases, which differ in the method of occurrence, course of disease, morphological changes and nature of transmission.
Various types of cystitis are classified into acute and chronic according to the nature of the course of the disease. We will consider two options for disease progression.
acute cystitis
In the context of the above symptoms, acute cystitis presents with low-grade fever and general malaise. The blood vessels in the bladder dilate, causing the walls of the organ to swell. In this case, spotting and hyperemia (Hyperaemia) were observed. During the acute phase of the disease, the mucosa and submucosa of the bladder are often damaged, their epithelium is sometimes rejected, and mixed blood may appear in the urine. Urine color in the bleeding form of the disease can vary from light pink to cloudy brown.
chronic cystitis
When the disease enters the chronic phase, inflammation expands and moves from the mucosa and submucosa to the muscular layer of the bladder. In this case, the color of the mucous membrane becomes white or light gray. If the disease is left untreated for a long time, a hardening process occurs in the organ, so its volume may decrease.
In the chronic form, all of the aforementioned signs can be "fuzzy" and vaguely expressed, making diagnosis difficult. If chronic cystitis is suspected, it is necessary to focus on the past medical history, macroscopic and microscopic examination of urine, cystoscopy, and bacteriological examination. Of particular importance in the detection of chronic cystitis is the concurrent gynecological examination, since it is often a genital infection that causes chronic cystitis.
Acute and Chronic Cystitis: Which Doctor Should I Contact?
Standard tests for diagnosing cystitis in older women, mature women, and girls are general urinalysis, urine culture for pathological flora (bacteriuria), and Nechiporenko analysis. As an added measure, modern clinics often offer bladder and kidney ultrasounds, cystoscopy and STI testing. In some cases, doctors may prescribe a urine sample for analysis, not through standard methods, but with a catheter. This may be necessary to prevent vaginal discharge from passing into the urine.
The treatment of acute cystitis is based on antibiotics. Since such drugs are excreted by the kidneys, the desired antibiotic concentration is readily achieved in the bladder, so the therapeutic effect occurs as quickly as possible. During this process, two important factors must be considered:
Doctors should prescribe antibiotics after receiving urine culture results, which will determine the susceptibility of the pathogen to the chosen drug.
Even after remission, the prescribed course of antibiotics should be taken to the end, which will avoid relapse and transition of the disease to a chronic form.

As an adjunct to the treatment of cystitis, use:
- Medications to relieve bladder spasms, generally anti-inflammatory drugs;
- physiotherapy;
- ozone therapy;
- acupuncture.
For the treatment of chronic cystitis, topical administration of drugs that prevent the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms can also be used. As an aid, tea tree oil gel can be used. The gel is recommended to eliminate vaginal discomfort, normalize the flora and restore the vaginal mucosa after infections and inflammatory diseases and after antibiotic treatment.
acute cystitis
It is worth noting that the treatment of acute cystitis is always bed rest. Treating bladder inflammatory processes "on the fly" without calling in sick, especially during the cold season, means running the risk that the disease may turn into a chronic form. This disease is always accompanied by severe stress on the body and the need for rest and rest. At the same time, ignoring the disease and delaying medical treatment can "lead to" pyelonephritis, the treatment of which requires constant medical supervision.
diet
In order to relieve inflammation as soon as possible, it is recommended to drink plenty of water: drink at least 1. 5 liters of fluids per day.
There are many nutritional limitations to cystitis. Eliminating the spicy and spicy will help recovery and prevent the situation from happening again. During treatment, it is necessary to completely exclude alcohol. This applies to all alcoholic beverages.
If you find yourself urinating painfully and frequently, with blood impurities, flakes, or pus in your urine, don't rush to panic. Indeed, according to statistics, female cystitis is a very common phenomenon.
The most important thing is not to waste time and seek medical attention in time.
Usually, the disorder is identified when there are often small amounts of painful fecal matter and blood impurities in the urine. Such a process is usually accompanied by an increase in body temperature. Cystitis is dangerous and may develop into a chronic form or the development of kidney inflammation. In most cases, cystitis is contagious.
Cystitis is common in both women and men, but due to the anatomy of the female body, fair sex is still more prone to the disease. The female urethra is shorter and wider than the male urethra, making it easier for pathogens to enter the bladder. This explains the common cases of cystitis in women. Women of childbearing age are most susceptible to cystitis. There are many cases of recurrent cystitis, which significantly deteriorates a woman's health and affects her life.
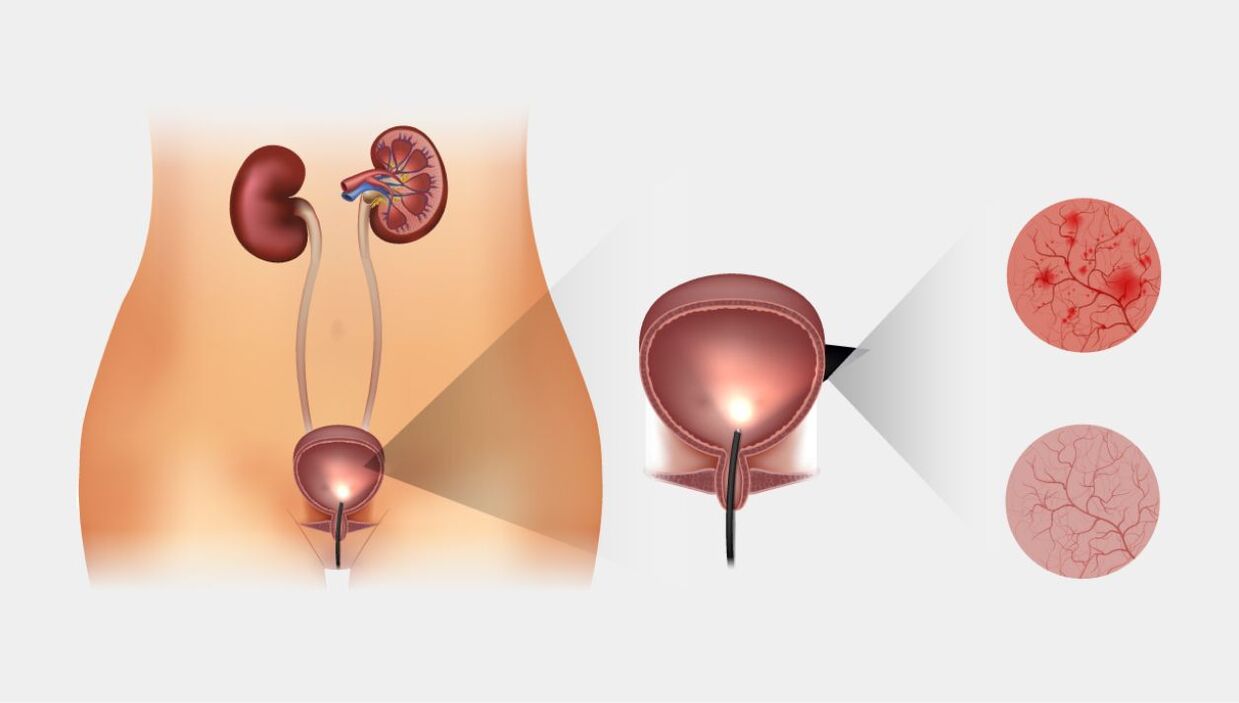
Prevalence of cystitis
The so-called acute cystitis is one of the most common diseases in urology. It is not uncommon to find uncomplicated cystitis, during which the microorganism affects only the mucosa, not the submucosa.
According to scientific research, it can be said that 26 to 36 million people suffer from acute cystitis every year in our country.
Girls are almost three times more likely to develop cystitis than boys. The disease is sometimes diagnosed in newborns and children under 1 year old, and is more common in children 1 to 3 years old, especially in children 13 to 15 years old. Typically, cystitis usually occurs in patients between the ages of 4 and 12.
Chronic cystitis is one of the most common urinary system diseases. According to these studies, chronic cystitis can be observed in 11-21% of the population. The significant dispersion of data is caused by the different approaches regarding the definition of chronic cystitis. A diagnosis of "chronic cystitis" should be considered when exacerbations occur 2 or more times a year, some study authors wrote.
Cystitis in summer
Few women don't feel the symptoms of cystitis themselves, when the joys of a wonderful summer day are overshadowed by this unpleasant disease. Also, in the summer, especially when women travel far from home and find themselves in an unusual environment, cystitis can arise for a variety of reasons.
In most cases, cystitis in summer is due to the following factors:
- Relocating to a new home during holidays, causing personal hygiene problems;
- hypothermia, which occurs as a result of prolonged bathing in cold water;
- Violation of usual urination habits, which is related to moving, flying or going to a new place;
- Severe climate change adversely affects human immunity.
Another factor that threatens the development of cystitis in some cases is increased sexual activity, which in the context of the aforementioned conditions is not good for the female body.
If your weekend or vacation is ruined by the occurrence of this unpleasant disease, it is necessary to make an appointment with a urologist as soon as possible. To confirm the diagnosis, you will need an ultrasound of the bladder, which is done with urine. Effectively acting directly on the causative agent of cystitis, today's antimicrobials can speed up the healing process and prevent acute cystitis from developing into a chronic form.
Compared to previous-generation drugs that affected a patient's entire body, modern drugs only affect the inflamed area of the bladder and have minimal impact on other body organs. The main concentration of the drug is shown to the greatest extent only in the inflamed urine and bladder mucosa. This allows you to minimize toxic effects on other organs and focus the entire burden on the management of cystitis.
Among the drugs used to treat this disease, it is worth noting the drugs used in combination with fosfomycin. He, given his high selectivity for action with minimal toxicological load on the body, possesses another useful quality - the drug does not subsequently cause phototoxicity. This is the name for a side effect caused by many drugs used to treat cystitis. Phototoxicity is manifested by increased sensitivity to sunlight, redness or burns occurring under the influence of even low-intensity UV light. Phototoxicity occurs due to the presence of substances with photosensitizer or photoreagent properties in the formulation. These substances can cause a lot of free radicals in the skin, which can lead to the destruction of skin cells, inflammation and even burns.
Unlike other drugs for cystitis, fosfomycin does not cause phototoxicity, which means it can be used without affecting planned beach vacation regimens. This advantage can also be referred to as the maximum absence of side effects, which makes it possible to safely and effectively treat cystitis in children and pregnant women.
cystitis during pregnancy
Gender Equity is often interested in the question of how the disease affects pregnancy. Bladder inflammation causes discomfort in all patients, and for women with weakened immune systems in this position, the disease is likely to be a severe test. Pregnant women facing symptoms of bladder inflammation have to go through a lot of trouble. Cystitis during pregnancy is undoubtedly dangerous, but prompt medical attention can prevent adverse consequences. Self-medication or neglect of the disease can lead to very serious complications, such as kidney infections. Bacteria can seriously damage them. Inflamed bladder mucosa can also negatively affect the fetus. Chances of premature birth and underweight.
Cystitis in children
It is widely believed that only adults are affected by cystitis, but this is not the case. Furthermore, there is no age limit for such diseases. Adults, children and the elderly can also get sick. Both men and women and very young patients suffer from cystitis, but the treatment of cystitis in children has its own characteristics.
Many times, cystitis in children occurs due to hypothermia. Bacteria are the main pathogens, and fungal and viral infections are extremely rare.
Causes of Cystitis
In 70-95% of patients with acute cystitis it is caused by Escherichia coli (E. coli), Staphylococcus saprophyticus is observed in 5-20%, and in the remaining patients Proteus mirabilis is the disease. ) and Klebsiella spp.
Usually, cystitis is caused by opportunistic flora. Studies have confirmed that the causative agent of cystitis is not necessarily bacteria, and cystitis is very likely to occur.
The high incidence of cystitis in women is due not only to the short length of the urethra, but also to its wider lumen and physiological position relative to other organs. Unlike the male urethra, the female urethra is closer to the anus. Due to this anatomical feature of the female body, the body is poorly protected from pathogenic microorganisms that enter the urethra, and then the microorganisms can easily migrate to the bladder, causing cystitis.
In men, cystitis is less common. The cause of this disease in men is usually inflammation of the urethra, epididymis, seminal vesicles, and prostate. It happened that the infection penetrated into the urethral area due to catheterization. The risk of cystitis doubles after bladder catheterization in men with BPH, of which frequent urinary retention is one of the symptoms. There is also an increased likelihood of developing cystitis after the introduction of a catheter into a pregnant woman or a woman who has just given birth, based on a decrease in urethral tone.
symptoms of cystitis
In adults, cystitis usually causes frequent, painful urination. The nature of the pain is described as a burning sensation. Urine changes, has a strong odor, becomes cloudy and contains blood impurities. At this point, health may deteriorate and persistent pain in the lower back can be felt. In older adults and children, symptoms of cystitis are usually less pronounced. They may be characterized by symptoms such as fever, abdominal pain, and nausea.
Diagnosis of cystitis
When diagnosing a disease, a urologist checks the results of a urinalysis as well as the results of a bladder ultrasound. To determine the cause of cystitis, they took bacterial urine cultures and swabs from the urethra. In most cases, bacteria of the opportunistic flora, i. e. , Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, E. coli, etc. , may be the cause of cystitis. Usually, cystitis is due to infection with sexually transmitted pathogens - Ureaplasma urealyticum and Mycoplasma. Treatment of cystitis involves the effect of drugs on infectious agents that may trigger the development of the disease.
Treatment of cystitis
If you do not delay the start of treatment, but use a sufficiently effective drug immediately, cystitis can be cured quickly and even the mucous membranes can be fully recovered. The chances of getting rid of cystitis completely will increase with the timely and correct diagnosis and the use of drugs that affect the center of the infection. Late initiation of treatment or prescribing treatment that only eliminates the symptoms of cystitis without affecting the pathogenic area can turn acute cystitis into chronic.

The main task faced by physicians treating cystitis is to destroy pathogenic microorganisms that have penetrated the bladder area and cause inflammation of the mucosa. The drug for the course of antibiotic treatment of the disease is determined according to the following parameters: the duration of the disease, the severity of the symptoms. In addition, possible side effects, the way and speed of excretion, the absorption of the drug, the presence or absence of other diseases, etc. are all taken into account when choosing a drug.
To date, there are relatively affordable treatments for cystitis that selectively affect the causative agent of the disease, and a qualified physician would recommend this treatment. When ingested, the drug concentrates in the bladder, which can increase its effectiveness. In addition, the use of modern antibiotics reduces the treatment time for cystitis, prevents side effects as much as possible, and reduces the risk to the entire patient's body.
Helpful Tips for Preventing Cystitis
- try to avoid hypothermia;
- Despite the situation, please follow the hygiene rules carefully;
- Use neutral and mild products when performing hygiene procedures;
- Change sanitary napkins in a timely manner;
- Go to the toilet on time without delay if necessary;
- Drink more water;
- It is recommended to give up tight clothes, tk. It can squeeze, worsen blood circulation in the pelvic area;
- Try to normalize bowel activity. If you are prone to constipation, it is recommended to increase your intake of fresh fruits and vegetables.
In this case, symptoms and treatment of cystitis are not a problem for you.